Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Funatsu, Takuya*; Kanai, Shun*; Ieda, Junichi; Fukami, Shunsuke*; Ohno, Hideo*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.4079_1 - 4079_8, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Modulation of the energy landscape by external perturbations governs various thermally-activated phenomena, described by the Arrhenius law. Thermal fluctuation of nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions with spin-transfer torque (STT) shows promise for unconventional computing, whereas its rigorous representation, based on the Neel-Arrhenius law, has been controversial. In particular, the exponents for thermally-activated switching rate therein, have been inaccessible with conventional thermally-stable nanomagnets with decade-long retention time. Here we approach the Neel-Arrhenius law with STT utilising superparamagnetic tunnel junctions that have high sensitivity to external perturbations and determine the exponents through several independent measurements including homodyne-detected ferromagnetic resonance, nanosecond STT switching, and random telegraph noise. Furthermore, we show that the results are comprehensively described by a concept of local bifurcation observed in various physical systems. The findings demonstrate the capability of superparamagnetic tunnel junction as a useful tester for statistical physics as well as sophisticated engineering of probabilistic computing hardware with a rigorous mathematical foundation.
Araki, Yasufumi; Ieda, Junichi
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.277205_1 - 277205_7, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:54.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Momentum-space topology of electrons under strong spin-orbit coupling contributes to the electrically induced torques exerting on magnetic textures insensitively to disorder or thermal fluctuation. We present a direct connection between band topology and the torques by classifying the whole torques phenomenologically. As well as the intrinsic anomalous Hall effect, the torques also emerge intrinsically from the anomalous velocity of electrons regardless of a nonequilibrium transport current. We especially point out the intrinsic contribution arising exclusively in magnetic textures, which we call the "topological Hall torque (THT)". The THT emerges in bulk crystals without any interface or surface structures. We numerically demonstrate the enhancement of the THT in comparison with the conventional spin-transfer torque in the bulk metallic ferromagnet, which accounts for the giant current-induced torque measured in ferromagnetic 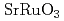 .
.
Oyanagi, Koichi*; Gomez-Perez, J. M.*; Zhang, X.-P.*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chen, Y.*; Sagasta, E.*; Chuvilin, A.*; Hueso, L. E.*; Golovach, V. N.*; Sebastian Bergeret, F.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(13), p.134428_1 - 134428_14, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:78.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kurebayashi, Daichi*; Araki, Yasufumi; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(8), p.084702_1 - 084702_9, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:68.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study current- and charge-induced spin torque in magnetic Weyl semimetals. In magnetic Weyl semimetals (WSM), topologically nontrivial band structure mediates anomalous coupling between magnetization and transport, making WSMs preferable for spintronics systems. In this paper, we determine all current-induced spin torques including spin-orbit torque and spin-transfer torque, up to first order with respect to spatial and temporal derivatives and electrical currents. We also calculate the charge-induced spin torque microscopically. We find the charge-induced spin torque originates from the chiral anomaly due to the correspondence between spin operators and axial current operators in our model.
Ieda, Junichi; Yamane, Yuta*
Physical Review B, 103(10), p.L100402_1 - L100402_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:78.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamane, Yuta*; Ieda, Junichi
Magune, 13(5), p.235 - 241, 2018/10
Ieda, Junichi; Yamane, Yuta*; Sinova, J.*
no journal, ,
Recently, antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials are generating more attention due to their potential to become a key player in technological applications. To understand spin transport in AFM metals, however, in addition to the s-d exchange interaction that plays a pivotal role in ferromagnetic-based spintronics, the sublattice degree of freedom should be taken into account. In this presentation we theoretically demonstrate electric voltage generation due to spinmotive forces originating from domain wall motion and magnetic resonance in antiferromagnets. This work suggests a new way to observe and explore the dynamics of antiferromagnetic textures by electrical means, an important aspect in the emerging field of antiferromagnetic spintronics. We also formulate spin-transfer torques in antiferromagnetic materials. Taking in the electron-magnetization exchange coupling and the inter-sublattice electron dynamic as model parameters, we examine the two limiting cases where either one of the two is dominant over another. Our work offers a framework for quantitative understanding of spin-transfer torques in different classes of antiferromagnetic materials.
Ieda, Junichi; Yamane, Yuta*; Sinova, J.*
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sakai, Takaki*; Yamanouchi, Michihiko*; Araki, Yasufumi; Uemura, Tetsuya*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi; Yamanouchi, Michihiko*; Sakai, Takaki*; Uemura, Tetsuya*; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi
no journal, ,
Araki, Yasufumi; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,